June 25 2024
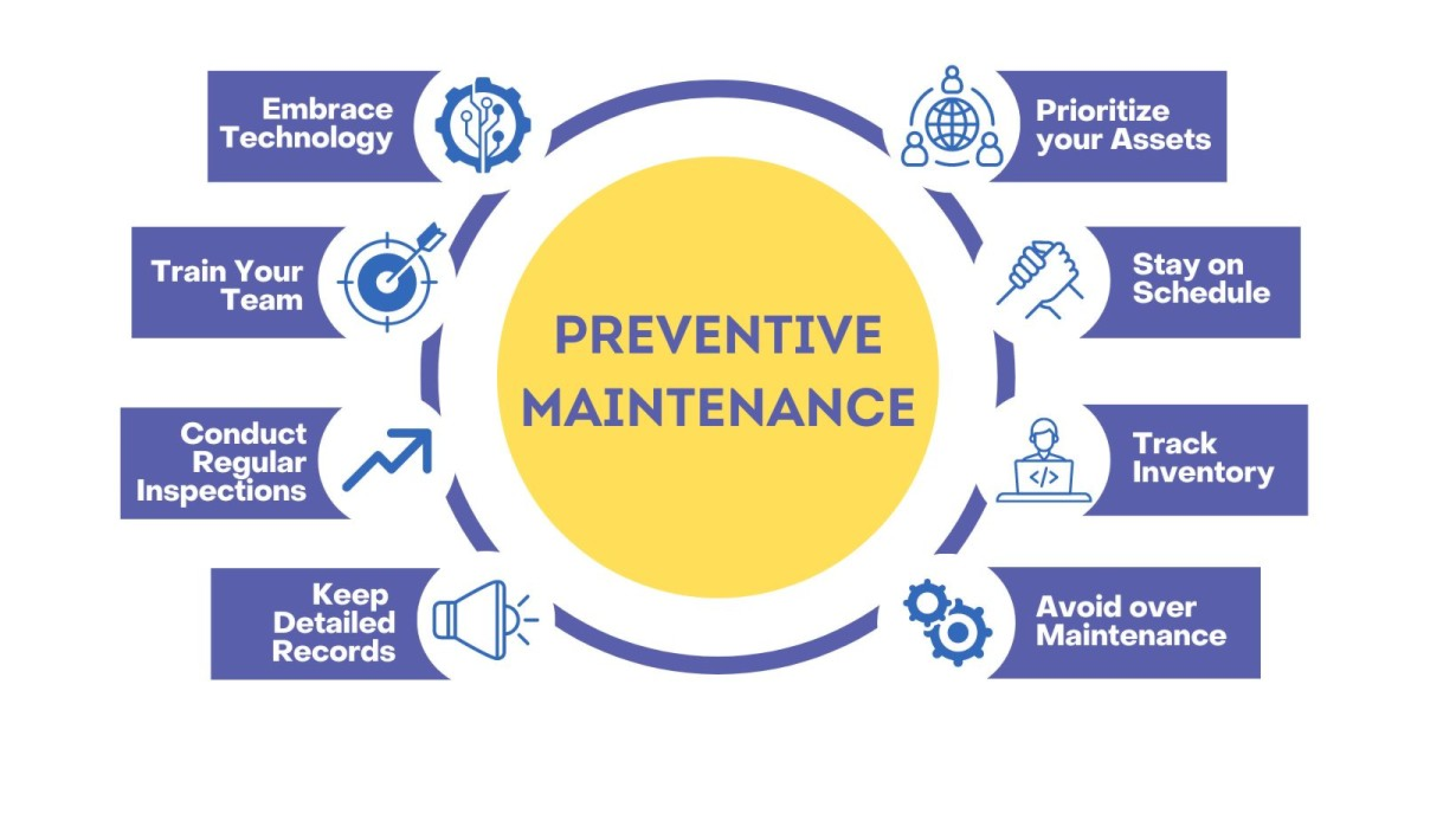
Maintenance and asset management are the backbone of any successful operation. But if you find yourself constantly battling unexpected equipment failures, it might feel like you’re always playing catch-up. Relying too much on reactive maintenance can lead to significant downtime, costly repairs, and even bigger headaches. Luckily, there’s a game-changer: preventive maintenance software. With the right tools, you can flip the script, stay ahead of problems, and save big on costs. Let’s dive into what preventive maintenance software is, how it works, and how to choose the best solution for your team.
What is Preventive Maintenance Software?
Imagine having a crystal ball that tells you when your equipment is about to break down—so you can fix it before it does. That’s essentially what preventive maintenance software offers. It’s a specialized tool designed to help organizations plan, schedule, and execute maintenance tasks before failures occur. By enabling a proactive approach, this software helps extend the life of your assets, minimize unexpected breakdowns, and optimize overall maintenance efficiency. Whether you're running a small facility or a large industrial operation, preventive maintenance software is your secret weapon for keeping equipment in peak condition and your operations running smoothly.
Why Preventive Maintenance Software is Essential
In today's fast-paced world, waiting for equipment to break down before you take action can spell disaster. Downtime not only grinds production to a halt, but also drives up maintenance costs and can even compromise safety. This is where preventive maintenance software comes into play. By allowing you to schedule routine maintenance tasks, monitor asset performance, and keep detailed records, this software ensures that minor issues are caught and addressed before they snowball into major problems.
Think of it like brushing your teeth to avoid cavities—preventive maintenance is all about keeping things clean and healthy so you don’t end up with a costly (and painful) root canal down the line. With maintenance software in your corner, you’re not just putting out fires; you’re preventing them from starting in the first place.
Types of Preventive Maintenance Software
Preventive maintenance software comes in all shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific needs within maintenance management and asset tracking. Let’s explore the most common types and how they can supercharge your operations.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
A CMMS is the beating heart of any preventive maintenance program. It helps your maintenance team keep a centralized record of all assets, equipment, and work orders. A CMMS automates and streamlines maintenance tasks, making it easier to plan, track, and optimize your entire maintenance operation.
Key Functions of a CMMS:
Automating Work Orders: Say goodbye to sticky notes and spreadsheets. A CMMS allows you to create, assign, and track work orders automatically, ensuring that maintenance tasks are completed on time.
Scheduling Preventive Maintenance: With a CMMS, you can schedule routine maintenance tasks based on time, usage, or condition triggers, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Maintenance scheduling has never been easier
Workflow Management: The software coordinates tasks, manages resources, and routes work orders to the right technicians, ensuring that nothing falls through the cracks.
Inventory Management: Keep track of spare parts and supplies to maintain optimal inventory levels and avoid stockouts. Your inventory management will be smooth sailing.
Reporting and Auditing: Generate detailed maintenance reports on activities, stay compliant with regulations, and breeze through audits with ease.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise CMMS: When choosing a CMMS, you’ll need to decide between a cloud-based solution, which offers greater flexibility and accessibility, or an on-premise solution, which provides more control over data and security.
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) Systems
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software is like a CMMS on steroids. It provides a comprehensive view of your organization’s physical assets throughout their entire lifecycle, from procurement to retirement.
Key Functions of an EAM System:
Asset Lifecycle Management: Track the entire asset lifecycle to make informed decisions about maintenance planning, repairs, and replacements.
Work Order Management: Automate and manage work orders with a broader focus on the entire asset lifecycle, not just day-to-day maintenance.
Inventory and Procurement: Coordinate asset inventory and procurement to ensure that spare parts and supplies are available when needed.
Labor and Resource Management: Optimize labor and resource allocation, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Performance Tracking: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your maintenance program and identify areas for improvement.
Asset Performance Management (APM) Systems
Asset Performance Management (APM) software takes asset reliability to the next level by integrating advanced technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence). APM systems analyze real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance scheduling.
Key Functions of an APM System:
Real-time Monitoring: Continuously monitor asset conditions, providing real-time insights into performance and potential issues.
Predictive Maintenance: Use data from IoT devices to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing you to perform predictive maintenance and schedule repairs before breakdowns occur.
Risk Management: Assess risks associated with asset performance, helping you prioritize maintenance tasks and allocate resources effectively.
Continuous Improvement: Leverage AI to learn from past maintenance activities and optimize future maintenance strategies.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software isn’t just for finance and HR—it’s also a key player in maintenance management. While ERP systems aren’t specifically designed for maintenance, they facilitate data integration and collaboration across your organization.
Key Functions of an ERP System:
Data Integration: Centralize data from multiple departments, ensuring everyone has access to accurate and up-to-date information.
Process Standardization: Standardize processes across the organization, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Inventory Management: By integrating with maintenance software, ERP systems help maintain accurate inventory levels and streamline procurement processes.
Financial Management: Track maintenance costs and budgets, providing insights into the financial impact of your maintenance program.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) software focuses on optimizing production processes by managing and monitoring activities on the factory floor. While MES is primarily concerned with production efficiency, it also plays a vital role in preventive maintenance by providing valuable data on equipment performance and usage.
Key Functions of an MES System:
Production Scheduling: Schedule production activities to ensure that resources are used efficiently and products are manufactured on time.
Data Collection: Collect data on equipment performance, production quality, and resource usage, providing insights into potential maintenance needs.
Process Optimization: Analyze production data to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements to the production process.
Resource Management: Manage the allocation of labor and materials, ensuring that resources are used effectively and costs are minimized.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems
SCADA systems are the eyes and ears of industrial processes, monitoring and controlling operations in real-time. While not exclusively designed for maintenance, SCADA systems are invaluable for preventive maintenance by collecting and analyzing data from equipment and sensors.
Key Functions of a SCADA System:
Real-time Monitoring: Monitor equipment conditions and process data from sensors, providing real-time insights into equipment maintenance needs.
Data Logging: Record data from equipment to track performance trends and identify potential maintenance needs.
Alarm Management: Generate alerts when equipment conditions deviate from acceptable parameters, enabling prompt corrective action.
Process Control: Allow operators to control industrial processes remotely, ensuring that equipment operates within safe and efficient parameters.
How to Choose the Right Preventive Maintenance Software
Selecting the right preventive maintenance software for your organization doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here’s how to make sure you pick the perfect tool for your needs:
1. Assess Your Maintenance Needs
Start by assessing your organization’s maintenance needs. Consider the size of your facility, the complexity of your equipment, and the specific challenges you face. This will help you determine which type of software is best suited to your requirements.
2. Consider Your Budget
Budget is always a key consideration when investing in new technology. While it’s important to choose a solution that meets your needs, it’s also essential to ensure that the software fits within your budget. Be sure to factor in not only the initial cost of the software but also ongoing maintenance and support costs.
3. Evaluate Ease of Use
The success of any software implementation depends on user adoption. Choose a solution that is intuitive and easy for your team to use. Consider whether the software offers training and support to help your team get up to speed quickly.
4. Look for Integration Capabilities
To get the most out of your preventive maintenance software, choose a solution that integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, like ERP or CMMS software. This will ensure that data flows smoothly between different departments and that you have a complete view of your maintenance operations.
5. Consider Scalability
As your organization grows, your maintenance needs will evolve. Choose software that can scale with your business, allowing you to add new assets, users, and functionality as needed.
Maximizing the Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Software
Once you’ve chosen the right preventive maintenance software for your organization, it’s time to maximize its benefits by integrating it with other systems and processes.
1. Integrate with ERP Systems
Integrating your preventive maintenance software with your ERP system can provide a complete view of your maintenance operations and ensure that all departments have access to the same information. This will help streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and reduce the risk of errors.
2. Use IoT and APM Technologies
Leverage IoT devices and APM systems to enhance the capabilities of your preventive maintenance software. By collecting real-time data from sensors, you can monitor equipment conditions more effectively and predict maintenance needs before they arise. This can lead to significant downtime reduction and maintenance cost savings.
3. Implement Comprehensive Maintenance Reporting
Use the data gathered by your preventive maintenance software to create detailed maintenance reports. These reports can provide insights into maintenance costs, equipment performance, and asset inventory status, helping you make informed decisions and continuously improve your maintenance strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between ERP and CMMS?
While both ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) are about managing your organization, they focus on different aspects. ERP is the all-encompassing system that handles everything from finances to HR, while CMMS zooms in on the maintenance aspect, managing work orders, equipment, and spare parts.
How is ERP different from EAM?
ERP connects the entire organization, ensuring all departments—from finance to the supply chain—are working with the same data. EAM (Enterprise Asset Management), on the other hand, focuses specifically on the lifecycle of physical assets, from procurement to disposal.
What sets CMMS apart from EAM?
CMMS handles the day-to-day maintenance tasks, such as scheduling work orders and tracking inventory. EAM, however, takes a broader approach, managing assets over their entire lifecycle and integrating more deeply with other business processes.
How do CMMS and SCADA systems work together?
SCADA systems monitor real-time equipment performance, while CMMS takes action based on that data. When SCADA detects an issue, it can alert the CMMS to create a work order, ensuring that maintenance is performed before the problem escalates.
What’s the difference between ERP and MES?
ERP is the overarching system that manages all business operations, while MES (Manufacturing Execution System) focuses specifically on optimizing production processes on the factory floor. MES ensures efficient production, while ERP ensures overall business coordination.
How do EAM and APM complement each other?
EAM manages assets throughout their lifecycle, while APM uses advanced analytics to monitor asset performance in real-time. Together, they provide a comprehensive asset management solution that helps you stay ahead of maintenance needs and optimize asset performance.
Can CMMS software integrate with ERP systems?
Yes, integrating CMMS with ERP creates a powerful synergy where maintenance operations are seamlessly linked with broader business processes, improving data accuracy and operational efficiency.